本文主要介绍【py2exe】和【pyinstaller】的使用。
【py2exe】下载地址:
http://www.py2exe.org/
【pyinstaller】 下载地址:
http://www.pyinstaller.org/downloads.html
python3.7 打包成exe程序(只需两行命令)
环境:pycharm2018.1+win7+python3.7
工具:pyinstaller
1、安装pyinstaller,cmd –> pip install pyinstaller
2、安装完成后,打开cmd,输入命令:pyinstaller -F *.py(星号为py文件的全路径,如下图)
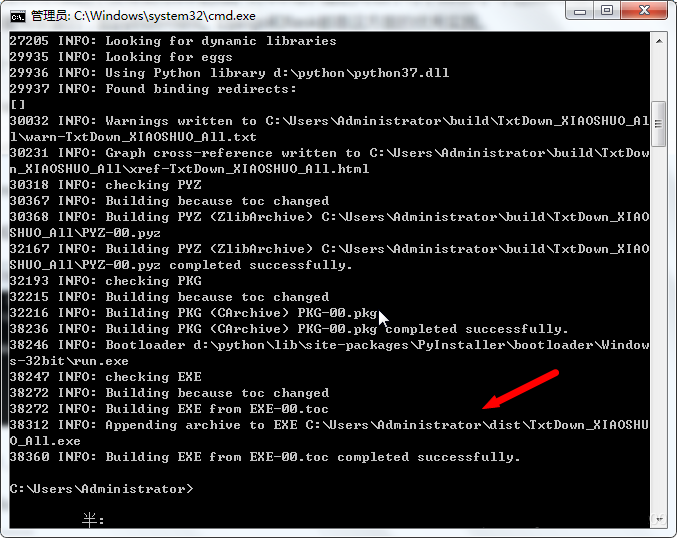
如下图显示,打包成功,会显示exe文件的位置,找到运行即可用。
我的py程序运行效果图:
py2exe使用方法 (含一些调试技巧,如压缩email 类)
一、简介
py2exe是一个将python脚本转换成windows上的可独立执行的可执行程序(*.exe)的工具,这样,你就可以不用装python而在windows系统上运行这个可执行程序。
py2exe已经被用于创建wxPython,Tkinter,Pmw,PyGTK,pygame,win32com client和server,和其它的独立程序。py2exe是发布在开源许可证下的。
二、安装py2exe
从http://www.py2exe.org下载并运行与你所安装的Python对应的py2exe版本的installer,这将安装py2exe和相应的例子;这些例子被安装在lib\site-packages\py2exe\samples目录下。
三、py2exe的用法
如果你有一个名为helloworld.py的python脚本,你想把它转换为运行在windows上的可执行程 序,并运行在没有安装python的 windows系统上,那么首先你应写一个用于发布程序的设置脚本例如mysetup.py,在其中的setup函数前插入语句 import py2exe 。
mysetup.py示例如下:
from distutils.core import setup import py2exe setup(console=["helloworld.py"])
如果显示错误提示的话 “ msvcp90.dll: no such file or directory”
请尝试下面的方法:
from distutils.core import setup
import py2exe
setup(
console=["helloworld.py"],
options = { "py2exe": { "dll_excludes": ["MSVCP90.dll"] } }
)
然后按下面的方法运行mysetup.py: (dos: cmd => cd desktop => mysetup.py py2exe)
python mysetup.py py2exe
上面的命令执行后将产生一个名为dist的子目录,其中包含了helloworld.exe,python24.dll,library.zip这些文件。
如果你的helloworld.py脚本中用了已编译的C扩展模块,那么这些模块也会被拷贝在个子目录中,同样,所有的dll文件在运行时都是需要的,除了系统的dll文件。
dist子目录中的文件包含了你的程序所必须的东西,你应将这个子目录中的所有内容一起发布。
默认情况下,py2exe在目录dist下创建以下这些必须的文件:
1、一个或多个exe文件。
2、python##.dll。
3、几个.pyd文件,它们是已编译的扩展名,它们是exe文件所需要的;加上其它的.dll文件,这些.dll是.pyd所需要的。
4、一个library.zip文件,它包含了已编译的纯的python模块如.pyc或.pyo
上面的mysetup.py创建了一个控制台的helloword.exe程序,如果你要创建一个图形用户界的程序,那么你只需要将mysetup.py中的console=[“helloworld.py”]替换为windows=[“myscript.py”]既可。
py2exe一次能够创建多个exe文件,你需要将这些脚本文件的列表传递给console或windows的关键字参数。如果你有几个相关联的脚本,那么这是很有用的。
运行下面个命令,将显示py2exe命令的所有命令行标记。
python mysetup.py py2exe –help
Global options:
--verbose (-v) run verbosely (default)
--quiet (-q) run quietly (turns verbosity off)
--dry-run (-n) don't actually do anything
--help (-h) show detailed help message
Options for 'py2exe' command:
--optimize (-O) optimization level: -O1 for "python -O", -O2 for
"python -OO", and -O0 to disable [default: -O0]
--dist-dir (-d) directory to put final built distributions in (default
is dist)
--excludes (-e) comma-separated list of modules to exclude
--dll-excludes comma-separated list of DLLs to exclude
--ignores comma-separated list of modules to ignore if they are
not found
--includes (-i) comma-separated list of modules to include
--packages (-p) comma-separated list of packages to include
--compressed (-c) create a compressed zipfile
--xref (-x) create and show a module cross reference
--bundle-files (-b) bundle dlls in the zipfile or the exe. Valid levels
are 1, 2, or 3 (default)
--skip-archive do not place Python bytecode files in an archive, put
them directly in the file system
--ascii (-a) do not automatically include encodings and codecs
--custom-boot-script Python file that will be run when setting up the
runtime environment
usage: setup_py2exe.py [global_opts] cmd1 [cmd1_opts] [cmd2 [cmd2_opts] ...]
or: setup_py2exe.py --help [cmd1 cmd2 ...]
or: setup_py2exe.py --help-commands
or: setup_py2exe.py cmd --help
四、指定额外的文件
一些应用程序在运行时需要额外的文件,诸如配置文件、字体、位图。
如果在安装脚本中用data_files可选项指定了那些额外的文件,那么py2exe能将这些文件拷贝到dist子目录中。data_files应包含一个元组(target-dir, files)列表,其中的files是这些额外的文件的列表。
示例如下:
PythonCode: # mysetup.py
from distutils.core import setup
import glob
import py2exe
setup(console=["helloworld.py"],
data_files=[("bitmaps",
["bm/large.gif", "bm/small.gif"]),
("fonts",
glob.glob("fonts\\*.fnt"))],
)
说明:data_files选项将创建一个子目录dist\bitmaps,其中包含两个.gif文件;一个子目录dist\fonts,其中包含了所有的.fnt文件。
五、Windows NT services
你可以通过传递一个service关键字参数给setup函数来建造Windows NT services
,这个service参数的值必须是一个Python模块名(包含一service类)的列表。
示例如下:
PythonCode: # mysetup.py
from distutils.core import setup import py2exe setup(service=["MyService"])
所建造的可执行的service是可以通过在其后跟一定的命令行参数标记来自行安装和卸载的。你可以通过在这个可执行的service(exe)后跟一-help参数来得到更多的帮助。
六、COM servers
你可以通过传递一个com_server 关键字参数给setup函数来建造Windows NT services
,这个service参数的值必须是一个Python模块名(包含一个或多个COM server 类)的列表。
示例如下:
PythonCode: # mysetup.py
from distutils.core import setup import py2exe setup(com_server=["win32com.server.interp"])
默认情况下,DLL和EXE servers被建造,你不需要它们的话你可以简单的删除它们。
一个标准的py2exe setup文件编写
-*- coding: cp936 -*-
from distutils.core import setup
import py2exe
includes = ["encodings", "encodings.*"]
#要包含的其它库文件
options = {"py2exe":
{"compressed": 1, #压缩
"optimize": 2,
"ascii": 1,
"includes":includes,
"bundle_files": 1 #所有文件打包成一个exe文件 }
}
setup(
options = options,
zipfile=None, #不生成library.zip文件
console=[{"script": "hello.py", "icon_resources": [(1, "hello.ico")] }]#源文件,程序图标
)
新 版本已经可以打包为一个文件了,以前都是一堆dll,pyd的。具体的变化其实只有一个地方。就是options里增加bundle_files项,值为 1表示pyd和dll文件会被打包到exe文件中,且不能从文件系统中加载python模块;值为2表示pyd和dll文件会被打包到exe文件中,但是 可以从文件系统中加载python模块。另外setup中使用zipfile=None可以不生成library.zip。
例如原来 的:
from distutils.core import setup
import py2exe
includes = ["encodings", "encodings.*"]
options = {"py2exe":
{ "compressed": 1,
"optimize": 2,
"includes": includes,
}
}
setup(
version = "0.1.0",
description = "search panda",
name = "search panda",
options = options,
windows=[{"script": "search.py", "icon_resources": [(1, "search.ico")] }],
)
只需要改为:
from distutils.core import setup
import py2exe
includes = ["encodings", "encodings.*"]
options = {"py2exe":
{ "compressed": 1,
"optimize": 2,
"includes": includes,
"bundle_files": 1
}
}
setup(
version = "0.1.0",
description = "search panda",
name = "search panda",
options = options,
zipfile=None,
windows=[{"script": "search.py", "icon_resources": [(1, "search.ico")] }],
)
比如,这里我打包以前的DelphiCode2HTML的
# -*- coding: gbk -*-
from distutils.core import setup
import py2exe
includes = ["encodings", "encodings.*"]
options = {"py2exe":
{"compressed": 1,
"optimize": 2,
"ascii": 1,
"includes":includes,
"bundle_files": 1}
}
setup(
options = options,
zipfile=None,
name = "HelloGuys.",
description = "this is a py2exe test",
windows=[{"script": "F:\我的程序\Python\CSDN Code Edit\Code2Html.py",
"icon_resources": [(1, "F:\书籍\我的图标\图标xp\Convert.ico")]
}]
)
下面列出他的一些 options
| keyword | description |
| data_files | list of “data” files that you are going to need to run your executable such as .pngs, .jpgs |
Py2exe extends Distutils setup keywords
In addition to the standard distutils setup keywords, the following py2exe keywords specify what and how to build.
| keyword | description |
| console | list of scripts to convert into console exes |
| windows | list of scripts to convert into GUI exes |
| service | list of module names containing win32 service classes |
| com_server | list of module names containing com server classes |
| ctypes_com_server | list of module names containing com server classes |
| zipfile | name of shared zipfile to generate; may specify a subdirectory; defaults to ‘library.zip’. If zipfile is set toNone , the files will be bundled within the executable instead of ‘library.zip’. |
| options | dictionary { “py2exe”: { “opt1”: val1, “opt2”: val2, … } } |
The options dictionary of py2exe
The option keyword takes the following set of dictionary key: value pairs. The dictionary “key” names and the “value” types are listed in the table below.
| key | value |
| unbuffered | if true, use unbuffered binary stdout and stderr |
| optimize | string or int of optimization level (0, 1, or 2) 0 = don’t optimize (generate .pyc) 1 = normal optimization (like python -O) 2 = extra optimization (like python -OO) See http://docs.python.org/distutils/apiref.html#module-distutils.util for more info. |
| includes | list of module names to include |
| packages | list of packages to include with subpackages |
| ignores | list of modules to ignore if they are not found |
| excludes | list of module names to exclude |
| dll_excludes | list of dlls to exclude |
| dist_dir | directory in which to build the final files |
| typelibs | list of gen_py generated typelibs to include |
| compressed | (boolean) create a compressed zipfile |
| xref | (boolean) create and show a module cross reference |
| bundle_files | bundle dlls in the zipfile or the exe. Valid values for bundle_files are: 3 = don’t bundle (default) 2 = bundle everything but the Python interpreter 1 = bundle everything, including the Python interpreter |
| skip_archive | (boolean) do not place Python bytecode files in an archive, put them directly in the file system |
| ascii | (boolean) do not automatically include encodings and codecs |
| custom-boot-script | Python file that will be run when setting up the runtime environment |
Example:
setup(
windows=['trypyglet.py'],
options={
"py2exe":{
"unbuffered": True,
"optimize": 2,
"excludes": ["email"]
}
}
)
For more information enter the following at the python command line:
>>> from distutils.core import setup >>> help(setup)
注意 windows 的用法,他可以代替 console, 如果你要集成 wxpython 的时候,一定会用的 !
更多请查看 http://www.py2exe.org/index.cgi/ListOfOptions
如果程序中含有email类,并且压缩时出现类似 “ImportError: No module named multipart ” 的错误,你需要如下的设置:
1. 尝试将Lib下的email包,复制到当前文件夹中
2. 把[’emai’] 放入includes中
3. 把[’email’]放入packages中
4. 继续运行py2exe
如:
from distutils.core import setup
import py2exe
includes = ["encodings", "encodings.*",'email']
options = {"py2exe":
{ "compressed": 1,
"optimize": 2,
"includes": includes,
"bundle_files": 1,
"packages": ['email'],
"dll_excludes": ["MSVCP90.dll"]
}
}
setup(
version = "0.1.0",
description = "3th",
name = "For My Lover",
options = options,
zipfile=None,
windows=[{"script": "love.py", "icon_resources": [(1, "roses.ico")] }],
)
python3.7 打包成exe的一种方法 pyinstaller
首先该方法是dos界面的,没有使用GUI的包。对GUI感兴趣的可以学习下tkinter。不过从web服务器的发展趋势来看,使用网页实现界面是最有前景的,即python+html。Django和flask都是这方面的优秀实践。
首先为啥说一定要注明是python3.7呢。因为之前的版本不支持pyinstaller。
环境:pycharm2018.1+win10+python3.7
工具:pyinstaller
1、使用pycharm安装pyinstaller,此处不写详细步骤,参考:
http://www.tianqiweiqi.com/pycharm-python-lib-install.html
找到pyinstaller安装即可。
2、找到pyinstaller的安装目录。
C:\Users\lounious\PycharmProjects\untitled\venv\Scripts\pyinstaller-script.py
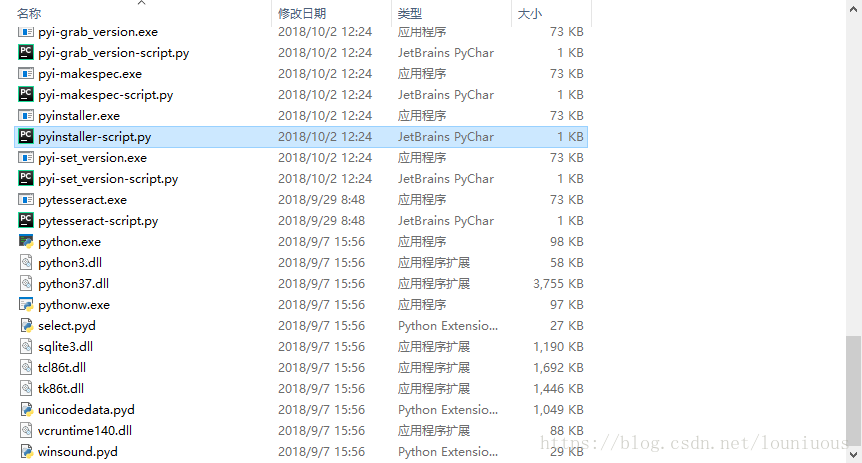
注意在该目录的母目录下一般有我们的程序文件
C:\Users\lounious\PycharmProjects\untitled
3、将我们要打包的程序copy至pyinstaller的安装目录下:
C:\Users\lounious\PycharmProjects\untitled\venv\Scripts\
4、打开cmd,找到该路径 cd C:\Users\lounious\PycharmProjects\untitled\venv\Scripts\,输入命令pyinstaller -F *.py
如下图显示,打包成功。
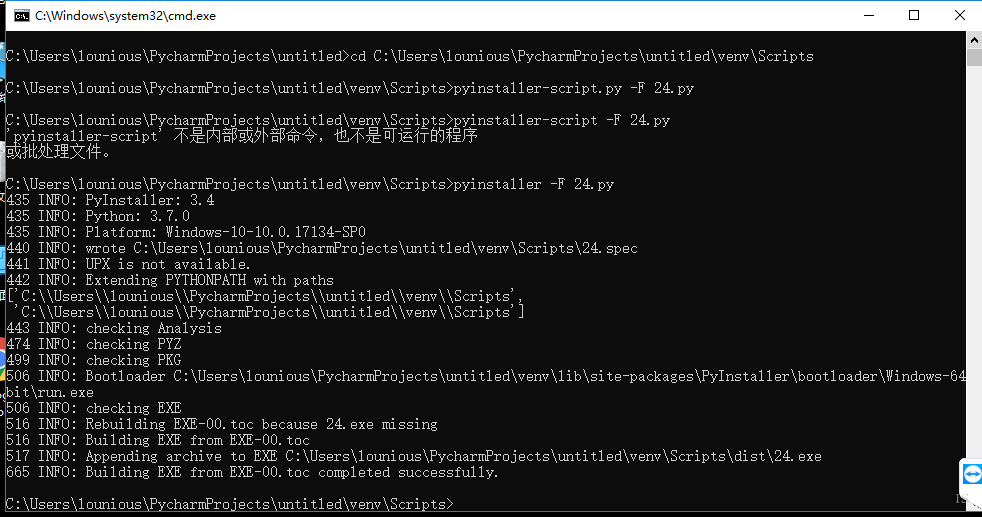
5、此时在Scripts的目录下能够看到已经生成的dist目录和*.spec文件。运行*.exe文件即可。
6、也可以使用命令pyinstaller -F *.py,该命令会将所有的依赖放到一个文件夹中。相当于-F的解压。

